|
Eczema or atopic dermatitis is a chronic skin condition often causing red itchy inflamed skin which can range in severity from mild to severe. According to statistics around 15 million people in the UK live with this condition and in 2015 GP’s in England wrote around 27 million prescriptions for various topical agents costing around £169 million. If you are thinking to yourself that more and more people are suffering from this you’d be right in your assumption. An NHS funded study has shown that the numbers of cases have risen by 40 % in 4 years. What we do know about the condition is that it is an allergic condition with 80% of sufferers having raised IgE antibodies. Eczema patients have positive allergy tests and around two thirds have a family history. Many also suffer from other atopic conditions such as asthma and hay fever. The standard treatment protocols involve simply managing symptoms via emollients and sometimes steroids and if infection is triggered due to scratching, antibiotics. Allergens are also tested for although these tend to focus on only IgE mediated reactions. Other considerations…. Immune function We are back to finding our root cause. So first lets look at what’s going on in the immune system. The allergy antibody IgE is elevated in 80% of cases and this is activated by a type of white blood cell, a helper cell called TH2. Mast cells can release higher amounts of histamine leading to the itch that we associate with eczema. Then there’s the issue that around 90% of sufferers also have a predominance of the bacteria Staphylococcus aureus on the skin which their immune system is unable to kill. Often scratching can activate this infection and cause some potentially severe staph infections. So how do we prevent this vicious circle? Well we have to do everything we can from day one to promote our gut/immune function. In our immune system we have regularly T cells sometimes known as Treg, which are involved in immune suppression and immune tolerance. It’s known that an unhealthy gut can lead to a decrease in these important cells and therefore an imbalance in our TH1/TH2 cells with the TH2 cells being unregulated. Studies have indicated that the use of probiotics from birth can confer a reduction in TH2 dominance and symptoms of AD at 13 months old versus placebo. Breast feeding Studies have shown that breast feeding is associated with a reduced risk of eczema and other allergies. However there is a caveat here in that although breast milk may confer antibody protection, in at risk children it may also be necessary for the feeding mum herself to remove common allergens which may unwittingly be triggering the problem as these proteins pass through the milk. Common allergens being dairy, peanuts and eggs. That said, the advice is to introduce these common allergens while breast feeding at the 6 to 12 month stage and to then continue to breast feed for a further 6 months following this introduction. Older and formula fed children In older and formula fed children a study looking at triggers for eczema indicated that Peanuts eggs and milk have been shown to account for 80% of adverse reactions to foods in people living wth contact dermatitis. Other common triggers and are wheat, fish and soy. The hygiene hypothesis. Are we just too clean? Epidemiological studies, especially those looking at migration from one country to another indicate that we acquire the same immune disorders as soon as we move to another area so environmental factors are playing a huge role. Lifestyle changes have led to a decrease in infection in the industrialised world and this has been shown to be inversely correlated with increases in allergies and autoimmunity. Studies have also shown that exposure to animals or growing up on a farm confers protection from a young age as we are exposed to a greater variety of bacteria which leads to activation and modulation of innate and adaptive immune response. In one large Swiss study, nearly 14,000 children were surveyed between 2006 and 2007, with over 3,000 farming children and around 11,000 non-farming children. In this study, 38% of the non-farming children had allergies compared to 19% of the farming children. Digestive compromise Those living with allergies have commonly got some level of digestive compromise and dysfunction. Stomach acid which normally assists in the removal of infection and therefore has a protective role, can commonly become low and therefore play a role in weakening our immune system and make us more prone to infection. It also sets us up potentially for the leaky gut phenomenon which puts us at risk of further food sensitivities of the IgG variety (delayed reaction) and chronic inflammation. If you have intestinal permeability you may also be experiencing other health challenges e.g. fatigue, brain fog, headaches, depression, sinus, IBS, reflux, joint pain, and autoimmunity. This is also why I see many clients in clinic who may be coming along for help getting to the root of their eczema but who also have any number of the aforementioned symptoms. A lack of a very important nutrient zinc can ensue as a consequence of low stomach acid. This nutrient is essential for immune, gut, hormone and skin health. It affects appetite, smell and taste of food, so in children who have a narrowing of food choices and are no longer enjoying certain foods, zinc deficiency may be at the heart of this. It is also a particular problem in cases of acne in teenagers so look out for changes in eating and appetite in older children and test their zinc levels. This can be done with a very simple taste test which all the family can do. Adequate zinc is also required for healing the gut. Gut Flora and probiotics Because our immune system resides primarily in the gut we need to look at gut bacteria. We also need to weed out any trouble makers Interestingly yeast overgrowth is a common cause of eczema. It’s also a very common problem as the western diet of high sugar, refined carbs and low fibre sets up the perfect conditions for this to grow. In addition, yeast overgrowth can result from long term medication use e.g. antibiotics, steroids and the oral contraceptive pill. We therefore need to ‘weed and seed’ the gut, get the infections out and the good bacteria in to assist with immune balancing and symptom resolution. Risk factors for allergies in children This relates to those factors which influence the health of the micro biome from day one. In an ideal world we need to be focusing on the gut health of mum prior to a planned pregnancy as this is what baby inherits. Areas of concern are
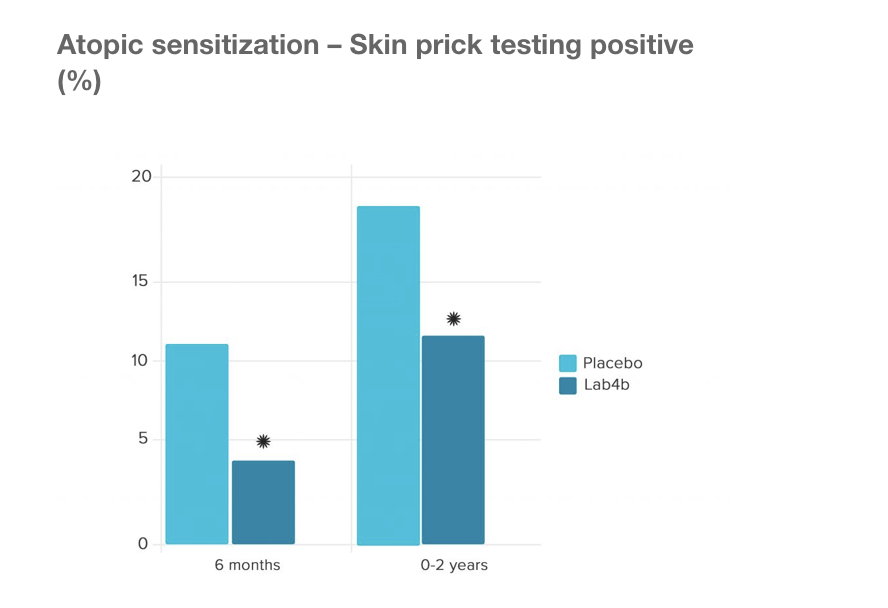
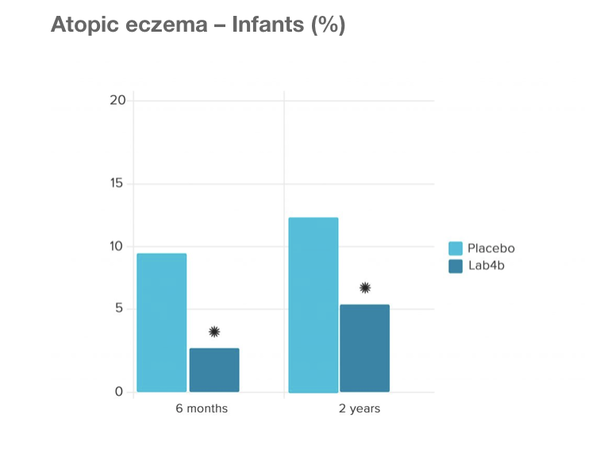
The Swansea Study This was a large study by the University of Swansea Medical School with 454 mother/baby pairs who were given Lab4b probiotics containing Lactobacilli and Bifidobacteria both during the final month of pregnancy and the first 6 months of infancy to evaluate whether this would prevent allergy in children. The results showed that versus placebo, the probiotic groups did indeed confer a protective effect on prevention of eczema and also prevention of allergic reaction to common allergens including pollen, cows milk, eggs and dust mites. Prof. Steve Allen, concluded the following key message from the trial:‘Lactobacilli and Bifidobacteria administered to pregnant women and infants aged 0-6 months prevented atopic sensitization and atopic eczema. The babies given the Lab4b probiotics were 57% less likely to develop atopic eczema than those receiving the placebo. The babies given Lab4b were 44% less likely to develop allergic reaction to common allergens, including pollen, cow’s milk, egg and house dust mite. Stress
Stress is very much linked with gut/immune function and when we are stressed we are more likely to have a flare of these conditions so managing stress for young and old is a life long strategy for eczema management. Adaptogen herbs can be helpful as can mindfulness, meditation and essential oils such as lavender for relaxation. As those living with eczema have a tendency towards poor absorption due to gut compromise a common nutrient which we can find ourselves low in is magnesium and this is also because we actually use more of it when we are stressed. More tips here on how to maintain levels. Nutritional therapy/ Functional medicine approach for eczema The nutritional therapy approach involved recognition of all of the above factors and follows through with the following stages.
Further testing This can be done if required and in addition to either allergy or food intolerance testing we can offer stool testing to identify infection and imbalance and even cortisol testing if stress is a particular trigger. Supplements This really does depend on the individual. It depends on what else they may be presenting with, their individual root cause/s, what medications they are on etc. However core supplements to include are going to be probiotics to reinoculate the gut, omega 3 and vitamin D. We may also recommend supplements and diet change to support gut integrity and immune balancing as per above recommendations. More info on booking an appointment with us for adults and children here. Referenced Studies Burks AW, Williams LW, Mallory SB, et al. Peanut protein as a major cause of adverse food reaction in patients with atopic dermatitis. Allergy Proceedings 1989;10:265-269. Von Mutius E, Vercelli D. Farm living: effects on childhood asthma and allergy. Nat Rev Immunol. 2010;10:861–868. Allen SJ et al 2014. Probiotics in the prevention of eczema: a randomised controlled trial. Archives of Disease in Childhood 99(11): 1014–1019
0 Comments
Leave a Reply. |
Amazon Associates DisclosureNourishing Insights is a participant in the Amazon EU Associates Programme, an affiliate advertising programme designed to provide a means for sites to earn advertising fees by advertising and linking to Amazon.co.uk. Archives
December 2023
|
WHAT OUR CLIENTS ARE SAYING“I did Nutritional Therapy with Beverley and it was life changing. I highly recommend it!” Allison Blakely (Glasgow)
|
Contact Us |